
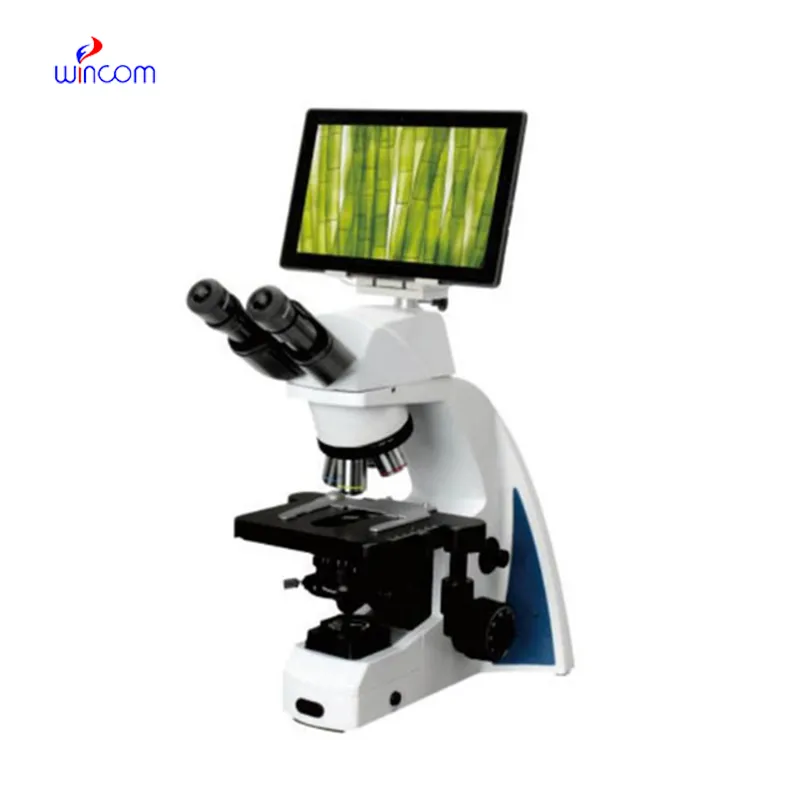
The Inverted Biological Microscope is engineered for precision and versatility, featuring adjustable magnification levels and ergonomic design for continuous use. Its optical system delivers uniform brightness and sharp focus on different specimens. Equipped with illumination controls within, the Inverted Biological Microscope maximizes contrast and clarity, enabling easier observation of delicate structures. Digital cameras and connectivity options for real-time image acquisition and sharing are included in most models. The Inverted Biological Microscope is built with durable materials to maintain stability of performance despite routine laboratory use.

The Inverted Biological Microscope is critical to science and manufacturing advancement. In the medical research arena, the Inverted Biological Microscope aids microscopic blood and tissue testing for accurate diagnostics. Research institutions use the Inverted Biological Microscope in cell culture analysis, detecting bacterial growth, and research on biofilms. Industrial laboratory environments utilize the Inverted Biological Microscope for product quality assurance and surface finishes evaluation. The Inverted Biological Microscope is also applied in environmental science to support monitoring of plankton populations and particles of pollutants, to enhance ecological studies and sustainability science.

The Inverted Biological Microscope will emerge hand in hand with revolutionary breakthroughs in computer science and optics. Future designs will incorporate ultra-sensitive detectors that can measure nanoscale motion in real-time. Through AI-aided enhancement, the Inverted Biological Microscope will facilitate predictive medicine and materials science analysis. Enhanced portability will allow researchers to employ small units on-site or at remote sites. As further technology emerges, the Inverted Biological Microscope will provide a critical portal for microanalysis and worldwide science networks.
In the interest of precision and reliability, the Inverted Biological Microscope should be constantly exposed to cleanliness and maintenance. Switch it off at all times before adjusting or cleaning parts. The lenses may be cleaned with alcohol-free cleaners lightly to avoid scratching. Rotary components such as knobs and stage mechanisms value light lubrication at regular intervals. The Inverted Biological Microscope must be stored away from direct sunlight and vibration. Professional checking once a year ensures optical alignment is not affected and prevents wear from invisible damage.
A Inverted Biological Microscope is able to closely study microorganisms, tissue, and materials and is thus a fundamental instrument in laboratories and classrooms. It operates by bending light or electron rays to enlarge specimens to appear gigantic many times magnification. The Inverted Biological Microscope has been enhanced with developments in optics to enable brighter, clearer, and digital-imaging-assisted magnification. In academic research work as well as industrial inspection, a Inverted Biological Microscope enables accurate analysis, recording, and examination of complex microscopic realms.
Q: What are the main parts of a microscope? A: The key components include the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, focusing knobs, and illumination system, all working together to magnify and clarify specimens. Q: How do you clean the lenses of a microscope? A: Lenses should be cleaned using soft lens paper or microfiber cloth with a small amount of lens cleaner to avoid scratching or damaging optical coatings. Q: What magnification levels can a microscope achieve? A: Depending on the model, a microscope can typically achieve magnifications ranging from 40x to over 1000x for detailed observation of microscopic structures. Q: Why is light adjustment important in a microscope? A: Proper light adjustment ensures accurate contrast and brightness, allowing clear observation without distortion or glare during viewing. Q: Can a microscope be used for educational purposes? A: Yes, microscopes are widely used in classrooms and laboratories to teach students about biology, materials science, and microscopic analysis.
This x-ray machine is reliable and easy to operate. Our technicians appreciate how quickly it processes scans, saving valuable time during busy patient hours.
The centrifuge operates quietly and efficiently. It’s compact but surprisingly powerful, making it perfect for daily lab use.
To protect the privacy of our buyers, only public service email domains like Gmail, Yahoo, and MSN will be displayed. Additionally, only a limited portion of the inquiry content will be shown.
Hello, I’m interested in your centrifuge models for laboratory use. Could you please send me more ...
Could you please provide more information about your microscope range? I’d like to know the magnif...
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +86-731-84176622
+86-731-84136655
Address: Rm.1507,Xinsancheng Plaza. No.58, Renmin Road(E),Changsha,Hunan,China